Extended Kalman Filter for 2D Localization
Designed and implemented an EKF for TurtleBot3 2D pose estimation (x, y, θ) by fusing a velocity-based motion model with GPS position updates and IMU yaw measurements. Validated performance using trajectory plots, consistency checks, and RMSE.
Project Overview
This mini project implements an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) for planar robot localization. The objective is to estimate the TurtleBot3 pose (x, y, θ) by combining a motion model with noisy sensor measurements.
What I Implemented
I designed an EKF that fuses a velocity-based motion model with GPS position updates and IMU yaw measurements. The filter predicts the robot state using the motion model and corrects the estimate when new sensor readings arrive.
Simulation Setup
I customized the TurtleBot3 Burger simulation by integrating a NavSat GPS sensor and configuring RTK-like noise settings. This allowed controlled evaluation of localization accuracy under different sensor noise conditions.
Evaluation and Validation
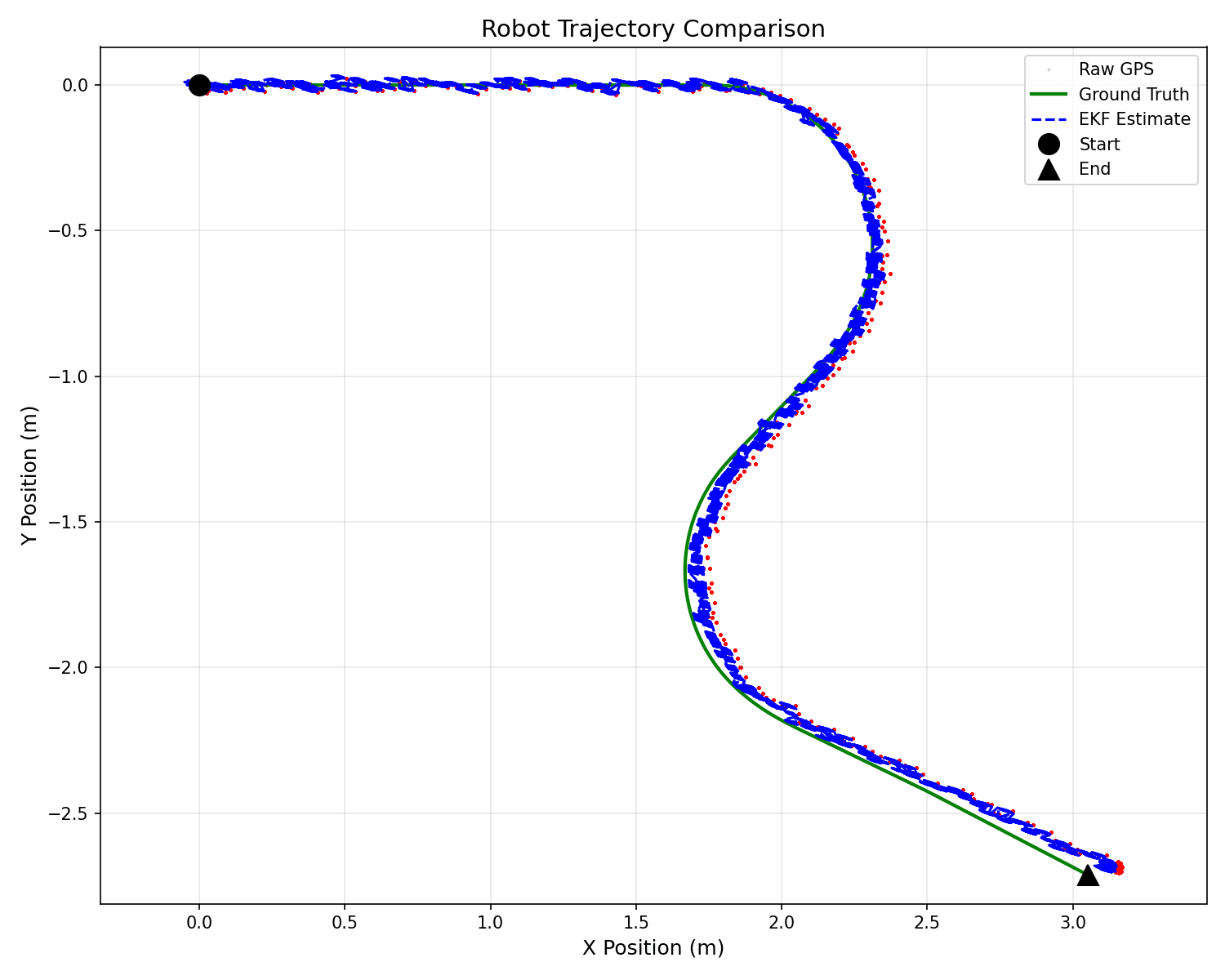
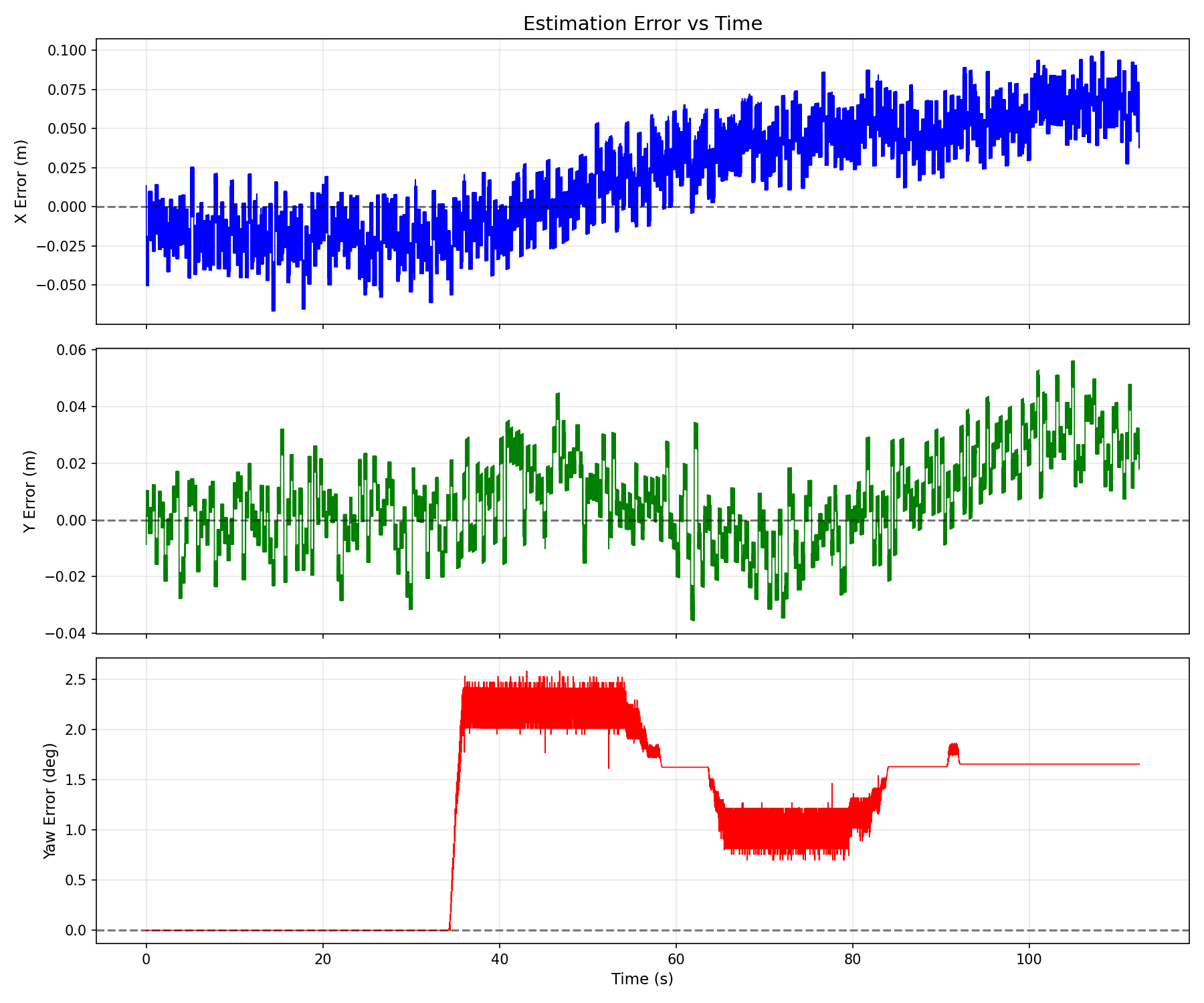
I logged ground truth, raw sensor outputs, and EKF estimates. Using these logs, I generated trajectory comparisons, error plots, covariance consistency (±2σ) plots, and RMSE metrics to validate filter performance and tuning.
Repository
Source code and setup instructions are available in the GitHub repository linked above.
Gallery